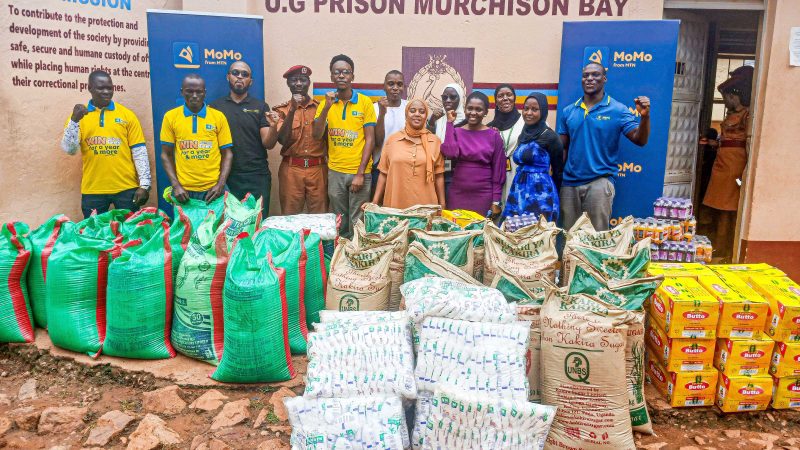
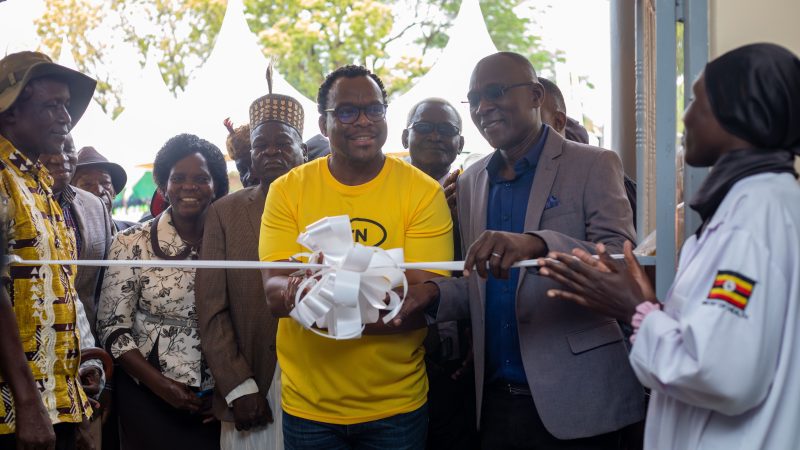
The East African Development Bank (EADB) in partnership with the British Council and the Royal College of Physicians have concluded yet another medical training of selected medical practitioners in Western Uganda.
The training which took place in Mbarara, is part of a medical training programme that EADB is carrying out across four East African countries aimed at curbing the increasing dangers of Cancer while also sensitizing communities in these countries. EADB’s aim is to train 600 medical professionals within a period of four years, to specialize in the treatment of cancer and neurological disorders.
The East African Development Bank’s Medical Training and Fellowship Programme (METAF) is an EADB initiative to build capacity in Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania and Uganda in the fields of neurology and oncology. EADB’s mission is to promote sustainable social-economic development in East Africa by providing development finance support and advisory services.
Through the Medical Training and Fellowship(METAF) Programme, EADB aims to increase capacity towards early detection, research and access to treatment of cancer and neurological disorders by increasing the number, quality and deployment of medical doctors in public service with specialty training in the treatment cancer and neurological disorders of in the East Africa region, especially in communities and areas where access to qualified professionals remains a challenge.
EADB is working in partnership with the British Council to manage and deliver the METAF Programme and with the Royal College of Physicians as the technical partner.
This is the fourth training taking place in Uganda. It follows similar trainings that were held St. Francis Hospital, Nsambya, at the Uganda Cancer Institute, Mulago in 2016 and in Soroti earlier this year. Other trainings have also taken place in Kenya and Tanzania.
There has been a recorded increase in the number of cancer patients in the region, and close to 80% of these patients find out when the cancer is in its late stages. Dr. Abrahams Omoding, a Specialist Medical Oncologist with the Uganda Cancer Institute and also one of the programme trainers says that Cancer now kills more people than HIV/AIDS, Malaria and Tuberculosis combined.
Although the signs and symptoms of the disease are still not well-known in many communities, there have been tremendous efforts to sensitize people and train medical practitioners in early identification of cancer cases.
The programme continues to focus on early detection, research and treatment of cancer and neurological disorders especially in communities where access to qualified professionals remains a challenge.
“This course is key in down staying late cancer detection. By training the doctors on the most important information on the signs and symptoms of cancer, we shall improve the ability to identify cancers at an early stage.” said Dr. Omoding.
Ms. Vivienne Yeda, the Director General of EADB reiterates that EADB’s course objective is to upgrade the ability of the target group of physicians to be able to better manage the patients with common neurological disorders.
“We are receiving positive feedback from the doctors who have so far taken part in the trainings. Through these doctors, we are surely having an impact. The fight against cancer should be taken up by all of us and as EADB we shall continue to train doctors until we meet our target of training 600 medical practitioners in four years.” Ms. Vivienne Yeda added.
Doctors who attended the medical training programme in Mbarara were in agreement for an increased need of such trainings across the region.
“I have learnt a lot of new things and through this training, I will now be able to look at medical cases from a different aspect so as I can be able to diagnose my patients with utmost surety.” said one of the doctors that took part in the training.
Non Communicable Diseases, are not passed from person to person. They are of long duration and generally slow progression. Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) and their risk factors are an emerging problem in East Africa although the focus has been directed to infectious diseases to a greater extent. EADB is thus extending a supporting arm so as to raise awareness of the severity of NCDs.
These diseases are driven by forces that include ageing, rapid unplanned urbanization, and the globalization of unhealthy lifestyles. For example, globalization of unhealthy lifestyles like unhealthy diets may show up in individuals as raised blood pressure, increased blood glucose, elevated blood lipids, and obesity. These are called ‘intermediate risk factors’ which can lead to cardiovascular disease, a NCD.
All age groups and regions are affected by NCDs. Very often, these illnesses are associated with older age groups, but evidence shows that 16 million of all deaths attributed to NCDs occur before the age of 70. Of these ‘premature’ deaths, 82% occurred in low- and middle-income countries.
Children, adults and the elderly alike are all vulnerable to the risk factors that contribute to Non-communicable diseases, whether from unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, exposure to tobacco smoke or the effects of the harmful use of alcohol.